Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare but aggressive type of skin cancer. It tends to grow quickly and can spread to other parts of the body (metastasize) if not treated promptly. AHN is here to help.

What is Merkel cell carcinoma?
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) develops in the Merkel cells, which are cells that live in the deepest layer of your epidermis (the outer layers of skin) and help regulate the touch sensation. Merkel cell carcinoma is known for its rapid growth and potential to spread to other parts of the body. Early detection is key for successful treatment.
Skin Cancer Center of Excellence
The AHN Melanoma and Skin Cancer Center of Excellence is unlike any other skin cancer center in the area. Our dedicated team of dermatologists, oncologists, oncodermatologists, and medical professionals are all working in tandem to provide the most comprehensive and compassionate care to our patients.
With a team of expert providers and state-of-the-art technology, we’re able to provide comprehensive skin cancer screening, diagnostic services, and specialized care for high-risk patients all in one setting to ensure consistent and thorough care.
Why choose AHN for Merkel cell cancer treatment?
At the AHN Cancer Institute, we see you as the individual you are who requires a specialized, tailored treatment plan that is delivered with compassionate care. When you choose AHN for your Merkel cell cancer treatment, you can expect care that is:
- Personalized: Our skilled team of dermatologists, oncologists, pathologists, dermatopathologists, and surgeons offer the latest targeted, minimally invasive surgeries or therapies pinpointed to treat Merkel cell cancer.
- Patient-centric: Our Navigation Team helps coordinate appointments, answers questions about symptoms and treatment options, and provides logistical support if you need to travel. We help lift the burden of logistics so you can focus on getting better.
- Compassionate: Cancer treatment is a stressful time. Our compassionate team of caregivers is devoted to improving your quality of life, helping you understand treatment options, and keeping you comfortable every step of the way. Our robust cancer support services help you live the best quality of life during treatment.
- Collaborative: Your treatment team works together to identify the right treatment for you, whether it’s surgery, medical oncology, or radiation therapy.
Merkel cell carcinoma symptoms and signs
Since Merkel cell skin cancer can be aggressive and spread quickly. It’s important to see your doctor right away if you notice any of the symptoms or signs, or if you are at higher risk for developing skin cancer. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving a cancer prognosis. Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is often found on sun-exposed areas like the face, head, neck and arms. It first appears as nodule or growth, often pink or red in appearance.
If you notice any new growths that have these characteristics or experience the following symptoms on an existing growth or nodule, contact your doctor immediately:
- Nodule: A firm, shiny, dome-shaped nodule, often flesh-colored, pink, or bluish-red usually in a chronically sun-exposed area of the skin.
- Rapid growth: The nodule may grow quickly, sometimes within weeks.
- Pain: The nodule may be painful or tender.
- Bleeding: The nodule may bleed easily.
- Ulceration: The nodule may ulcerate or break open.
- Lymphadenopathy: Swollen lymph nodes near the tumor.
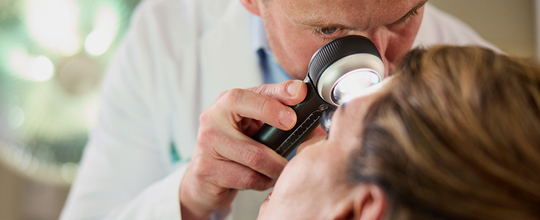
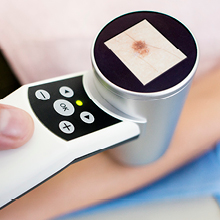

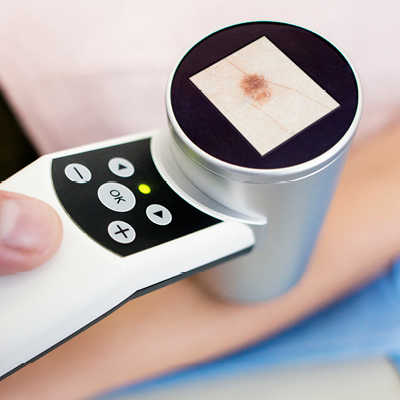
Merkel cell carcinoma risk factors
While Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is rarer than other skin cancers, there some key risk factors that can play a significant part in its development. If you know you are at greater risk or experience any of the following, talk to your doctor about being screened:
- Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCV): This is a common virus that people can get and doesn’t always contribute to Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC), but it is known to play a role in developing MCC.
- Age: MCC is more common in older adults, usually 50 years of age and older.
- Sun exposure: History of exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun or indoor tanning can increase the risk of MCC.
- Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or who have had an organ transplant, are at increased risk.
- Fair skin: People with fair skin, freckles, and a history of sunburns are more at risk for developing MCC.
- Exposure to certain chemicals: Exposure to arsenic and certain other chemicals may increase the risk of MCC.
Merkel cell carcinoma screening and diagnosis
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is aggressive and can spread quickly. Knowing your risk factors, early detection, and treatment offer the best chance of survival. Ways to reduce your risk of MCC include:
- Regular skin exams: Check your skin regularly for any changes and see a dermatologist for annual skin exams. If you are at greater risk for developing MCC, contact your doctor right away if you notice changes in your skin.
- Sun protection: Wear sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, protective clothing with built in UPF and UVA/UVB protection, and avoid prolonged sun exposure, especially during peak hours.
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, to support your immune system, since a weakened immune system can increase risk of MCC.
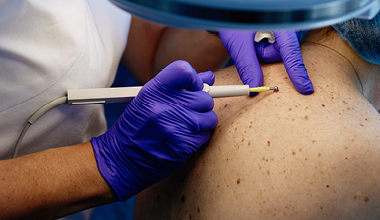


Diagnosing Merkel cell carcinoma
It is important to catch Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) early as it can rapidly spread to other parts of the body. At AHN, the diagnosis of MCC is often confirmed and treated by a multidisciplinary team of specialists, including dermatologists, pathologists, oncologists, and surgeons. Depending on the appearance and location of the cancer, there are numerous diagnosis tools we can use. At AHN, we are here to support you through your treatment plan with comprehensive and compassionate care.
At AHN, we use a multidisciplinary approach to care. The first step in diagnosing Merkel cell carcinoma is often a physical exam and a review of your health history. From there, we will conduct different diagnostic tests, including blood tests, biopsies, and, if needed, imaging.
Blood tests
Blood tests will help your care team look for markers that indicate the presence of Merkel cell carcinoma. Your doctor can determine which type of test will provide the information that’s necessary to guide your treatment.
Biopsy
In conjunction with the appropriate blood tests, your doctor may want to do a biopsy of the nodule. In this procedure, some or all of the nodule will be removed to be tested and examined under a microscope. There are different types of biopsies that your doctor might conduct.
- Punch Biopsy: A small sample of tissue is removed from the lesion using a small circular instrument.
- Excisional Biopsy: The entire lesion is surgically removed and sent for analysis.
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA): A thin needle is used to extract cells from the lesion.
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: If the tumor is larger or located in a high-risk area, a sentinel lymph node biopsy may be performed to check for spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Imaging tests
Imaging tests play a crucial part in identifying the presence of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). An imaging test can offer an in-depth look into the extent of the cancer.
- CT scan or MRI: These imaging tests can help determine the extent of the tumor and whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs.
- PET Scan: This scan can detect metabolically active cancer cells, which can help identify the presence of metastases (if the cancer has spread).
Your doctor may determine you need additional testing. Other tests for MCC may include:
- Microscopic analysis: The biopsy sample is examined under a microscope by a pathologist. AHN pathologists and dermatopathologists are highly trained and skilled. They will examine the sample for the characteristic features of MCC, such as small, round cells with dense nuclei and a specific arrangement.
- Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCV) testing: Immunohistochemistry (the study of the chemistry in the immune system) is used to detect the presence of MCV in the tumor cells. Most MCC cases are positive for MCV, which supports the diagnosis.
Stages of Merkel cell carcinoma
Once your care team has the results from your tests and your biopsy has been examined, we will have the information necessary that can indicate the type and stage of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC).
The majority of MCC cases are positive for Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCV), suggesting a viral role in tumor development. A smaller percentage of MCC cases are negative for MCV, and these may have different clinical characteristics and treatment responses.
It is also important to determine if the cancer is confined to the original site, or primary MCC. If the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes, lungs, bones, or liver, it is categorized as metastatic MCC. Your AHN doctor will help you understand your diagnosis and care plan.
Staging levels
MCC is staged using the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system, which considers the size of the tumor, the depth of invasion, the number of lymph nodes involved, and whether the cancer has spread to distant sites.
MCC stages look like:
- Stage I: The tumor is small and localized, confined to the skin.
- Stage II: The tumor is larger than 2 cm or has invaded underlying tissue below the skin, such as the muscle fascia, cartilage, or bone.
- Stage III: The tumor has spread to lymph nodes.
- Stage IV: The tumor has spread to distant organs, such as the lungs, liver, or bones.
Merkel cell carcinoma treatment
Your treatment for Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) will depend on the type and stage you have. Your AHN care team of dermatologists, oncologists, and other specialists will help you understand each step and connect you with the resources you need to feel supported and cared for. Your treatment options could include:
- Surgery: This is the primary treatment for localized — meaning hasn’t spread — Merkel cell carcinoma. The tumor and a margin of healthy tissue surrounding it is removed.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy rays are directed at the tumor site. This is often used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells or as the primary treatment for tumors that cannot be surgically removed.
- Chemotherapy: Used to treat metastatic or advanced MCC, drugs are administered intravenously or orally to reach cancer cells throughout the body.
- Immunotherapy: Using the body’s own immune system to fight the cancer, this is an innovative and growing area of cancer treatment.
- Targeted therapy: This treatment uses specific drugs to limit or slow cancer growth and proteins.
Merkel cell carcinoma FAQs
A skin cancer diagnosis like Merkel cell carcinoma will likely bring about many questions. AHN is here to help you find answers and resources that are specific to your diagnosis. To help you get started and reduce some of the overwhelm, we’ve included answers to some of our patients most frequently asked questions. Your care team will be available to answer any and all questions you may have, but these might help you feel a little more informed.
What does Merkel cell carcinoma look like?
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) typically appears as a firm, shiny, dome-shaped nodule or lump on the skin. It often has a red, pink, or purplish color and can sometimes be tender to the touch. These lesions usually grow rapidly and are often found on sun-exposed areas like the head and neck, but also on arms, legs, and trunk. Unlike some other skin cancers, MCC usually does not present as an open sore or a changing mole. The acronym AEIOU can help remember its characteristics: asymptomatic, expanding rapidly, immune suppression, older than 50, and UV exposed site.
What are the early signs of Merkel cell carcinoma?
The early signs of Merkel cell carcinoma are often subtle but important to recognize due to its aggressive nature. The primary early sign is the appearance of a new, firm, rapidly growing, painless skin lump or nodule. This lump is typically flesh-colored, red, or purplish. It may be mistaken for a cyst, insect bite, or common pimple. Because it's usually painless (asymptomatic), people might overlook it, which is why rapid growth is a key indicator to watch for.
Is Merkel cell carcinoma contagious?
No, Merkel cell carcinoma is not contagious. You cannot catch it from another person. While a virus (Merkel cell polyomavirus) is strongly linked to the development of MCC in many cases, this virus is very common and typically harmless. The development of MCC is complex and involves factors like immune suppression and UV exposure in addition to the virus. Having the virus does not mean you will get MCC, and the cancer itself does not spread from person to person.
How long does it take for Merkel cell carcinoma to metastasize?
Merkel cell carcinoma is known for its aggressive nature and high potential for early metastasis (spread). It can spread to nearby lymph nodes and distant organs relatively quickly, sometimes within months of initial appearance. The exact time frame can vary significantly between individuals and depends on factors like the tumor's size, depth, and the patient's immune status. This rapid spread potential is why early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for improving outcomes.
How curable is Merkel cell carcinoma?
Merkel cell carcinoma can be curable, especially when detected and treated at its earliest stages before it has spread. For localized MCC, surgical removal, often combined with radiation therapy, can lead to good outcomes. However, MCC has a high rate of recurrence and metastasis, making it more challenging to cure once it has spread. Advances in immunotherapy have significantly improved the prognosis for some patients with advanced or metastatic MCC, leading to long-term control and even remission in some cases.
How treatable is Merkel cell carcinoma?
Merkel cell carcinoma is highly treatable, though the treatment approach depends heavily on the stage of the cancer. Common treatments include:
- Surgery: To remove the primary tumor and often includes a sentinel lymph node biopsy to check for spread to regional lymph nodes. For more advanced cases, a larger lymph node dissection may be performed.
- Radiation Therapy: Often used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells in the treated area or for cases where surgery isn't feasible.
- Immunotherapy: A significant breakthrough in recent years, this uses drugs that help the body's immune system fight the cancer. It is often the first-line treatment for advanced or metastatic MCC.
- Chemotherapy: Less commonly used as a primary treatment now compared to immunotherapy, but may be considered in specific situations. The goal is to personalize the treatment plan based on the individual's specific MCC characteristics and overall health.
What is the life expectancy of someone with Merkel cell carcinoma?
The life expectancy for someone with Merkel cell carcinoma varies significantly depending on the stage at diagnosis, the patient's immune status, and their response to treatment.
- For localized MCC, the prognosis is generally better, with five-year survival rates ranging from approximately 50–70%.
- If the cancer has spread to regional lymph nodes, the five-year survival rate typically decreases to around 30–50%.
- For distant metastatic MCC, the prognosis is much more challenging, though recent advances in immunotherapy have dramatically improved outcomes for some patients, leading to longer survival times than previously observed. It's important to discuss your specific prognosis with your care team, as they can provide the most accurate information based on your individual circumstances.
Contact us
Call the Hope Line at 412-578-HOPE 412-578-4673 to connect with a nurse navigator or schedule an appointment.
Book a screening
Screenings let us find cancer early when it’s most treatable. Schedule a skin cancer screening near you during a weekday or during a Saturday screening time.
Second opinions
If you have cancer, you have a team of oncology specialists ready to review your medical records and offer you a second opinion. After completing their review, they’ll talk with you about your goals to determine a course of treatment that’s right for you. To get started, fill out our Second Opinion Request form. A nurse navigator will contact you within the next 24 to 48 hours to discuss next steps and schedule.

